Gemstone Testing Laboratory
Diamond Testing Lab
The laboratories of GTL commercializes the sophisticated systems and devices that are conceived, designed and fine-tuned inhouse. They are brought to the market for the benefit of the diamond industry and trade around the globe. Innovation, quality, user-friendliness and service are keywords in GTL’s business strategy. Its products include highly specialized microscopes, cutting machines and devices that can efficiently screen for treated synthetic diamonds & coloured stones.
COMMON SOLUTION FOR YOU
Question & Answer
Gemstone identification is the process of determining the exact type of a gemstone. Our gemologists utilize a combination of advanced instruments and their expertise to identify the specific mineral species of your gemstone. This helps distinguish natural stones from synthetics or imitations and can also reveal treatments a stone may have undergone.
A gemstone certificate from a reputable lab like GEM TESTING LAB serves as an unbiased and independent assessment of your gemstone’s qualities. It provides a detailed report on the stone’s identification, weight, cut, clarity, color, and any treatments detected. This certificate enhances the value and authenticity of your gemstone, fostering trust during transactions and potentially increasing resale value.
Several factors influence a gemstone’s value, including:
- Gemstone type: Different gemstones have inherent value based on rarity, demand, and historical significance.
- The 4Cs (for diamonds): Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight all play a crucial role in determining a diamond’s value. Similar principles apply to other gemstones, though specific factors may vary.
- Treatments: Some treatments can enhance a gemstone’s appearance but may also affect its value. A reliable certificate will disclose any treatments detected.
- Origin: The geographical source of some gemstones can influence their value due to rarity or unique characteristics associated with specific locations.
The turnaround time for gemstone testing can vary depending on the complexity of the analysis and the workload at our lab. However, we strive to deliver your report within a timeframe of (mention your typical turnaround time). For urgent requests, please inquire about expedited service options (if available).
The cost depends on the type of service requested (identification, certification, valuation) and the gemstone itself. We offer competitive rates and may have package deals for clients requiring multiple services.
We recommend contacting us to discuss the submission process. This may involve scheduling an appointment or following specific packaging and shipping procedures to ensure the safe arrival of your gemstone. Or you can directly visit our store.
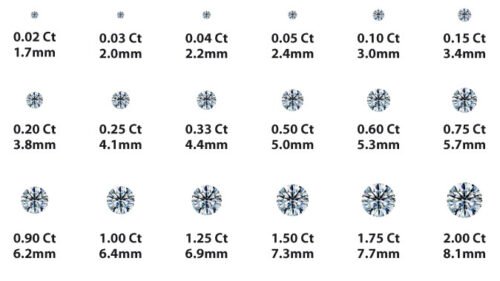
Diamond Carat
Carat is the term used to describe the weight of any gemstone, including diamonds. Although the definition of a carat has changed over time, since 1913 the international standard has been 200 milligrams, or 1/5 of a gram.
Diamonds can range in size from a fraction of a carat to several carats. Given the rarity of large stones, however, the price increases rapidly with size; therefore, a single 2-carat diamond will cost much more than two 1-carat diamonds. Very large diamonds with good color and clarity are very rare.
Below is the IDT Diamond Color Chart with definitions
Diamond Color
Diamonds come in a variety of colors, some of them highly prized (pinks, blues, even yellow). However in a white diamond, the presence of a yellow tint will lower the price of a diamond. The less body color in a white diamond, the more true color it will reflect, and thus the greater its value. IDT grades diamonds on a scale of D to N.
Below is the IDT Diamond Color Chart with definitions
| Colorless | While there are differences in colour between D, E, and F diamonds, they can be detected only by a gemologist in side by side comparisons, and rarely by the untrained eye. D-F diamonds should only be set in white gold / platinum. Yellow gold reflects color, negating the diamond’s colorless effect. | |
| Near Colorless | While containing traces of color, G-J diamonds are suitable for a platinum or white gold setting, which would normally betray any hint of color in a diamond. Because I-J diamonds are more common than the higher grades, they tend to be a great value. An I-J diamond may retail for half the price of a D diamond. Within the G-J range, price tends to increase 10-20% between each diamond grade. | |
| Faint Color | Beginning with K diamonds, color (usually a yellow tint) is more easily detected by the naked eye. Set in yellow gold, these warm colored diamonds appeal to some, and are an exceptional value. Others will feel they have too much color. Due to its perceptible color tint, a K diamond is often half the price of a G diamond. | |
| Light Color | Diamonds in the N-R color range have an easily seen yellow or brown tint, but are much less expensive than higher grades. Lumera does not carry diamonds in this color range due to a lack of demand. If you desire a diamond in this range, request a price quote using the custom diamond search. |
Diamond Cut
A diamond cut is a style or design guide used when shaping a diamond for polishing such as the brilliant cut. The cut of a diamond greatly affects a diamond’s brilliance; this means if it is cut poorly, it will be less luminous.
Below is the IDT Diamond Cut Chart with definitions
| Round Brilliant cut |  | This is referred to as the archetypical brilliant cut that features a total of 58 facets which is the optimal number that is used to achieve maximum light return. |
| Oval Brilliant Cut |  | This is a narrower and longer version of the round brilliant cut. |
| Marquise Diamond Cut |  | This is one of the types of diamond cuts that are similar to an oval shape. It can be described as an elongated version of the round option but features more pointed ends. This is a great shape that is used to make a persons finger appear as though they are thing and long. |
| Pearl Diamond Cut |  | This also has 58 facets like the round brilliant cut but usually has varying proportions. It is quite similar to the marquise and oval shapes but comes with a soft and round edge. |
| Heart Diamond Cut |  | This is one of the most romantic types of diamond cuts in the market. Forming the shape perfectly is normally a difficult task as all the lobes have to be totally symmetrical to achieve diamond brilliance. |
| Trilliant Diamond Cut |  | This is a triangular shaped diamond that is normally used to enhance larger stone centers working as side stones. |
| Emerald Cut |  | This is a rectangular shaped stone that has an open and large table which offers additional clarity. |
| Baguette Cut |  | This is used as stone whose main purpose is to accentuate a larger piece of center stone. |










